Saskatchewan Education, 1985, p.6.
Teaching Models- Represent the broadest level of Instructional Practices
Strategies Vs. Methods
Strategies determine the approach to achieve a learning objective
Method- Specific ways of creating learning environments. How will the teacher and students be involved? How will they work together to achieve the learning objective and goals?
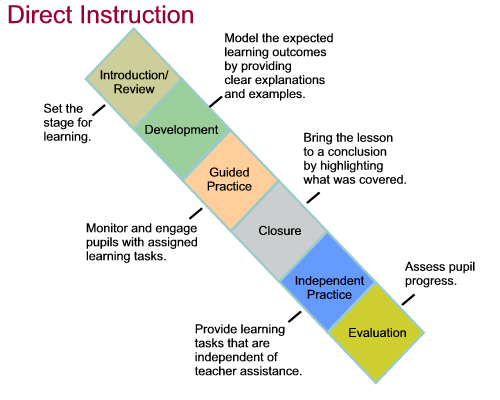
Direct Instruction is teacher directed. It involves lectures (20% of lesson time), guided practice and independent activities.
Indirect Instruction can use storytelling and oral tradition and is commonly used in ELA.
Inquiry- Students exploring a problem. Students found a problem, question and hypothesis and explore and experiment to form a conclusion and share their findings.
Cooperative Learning- Allows students to work together and build off each other's answers to answer questions and explore topics.
Independent Study- analyze problems reflect, make decisions and can be used in science journals.
Research Projects- can be done individually, with a partner or a groups. Students explore one problem or topic in depth.
Authentic Assessment- What can be assesses? Readiness, Interest and Learning Profile. Assessments can include pre-assessment, formative assessment and summative assessment.






No comments:
Post a Comment